Ipsilateral And Contralateral Central Nervous System
Ipsilateral and contralateral central nervous system. Central Projections o f the retina The retina projects to four subcortical regions in the brain. The peripheral nervous system PNS is formed by neurons of the cranial and spinal nerves. Also used to compare the location of structures are the opposite terms superior and inferior.
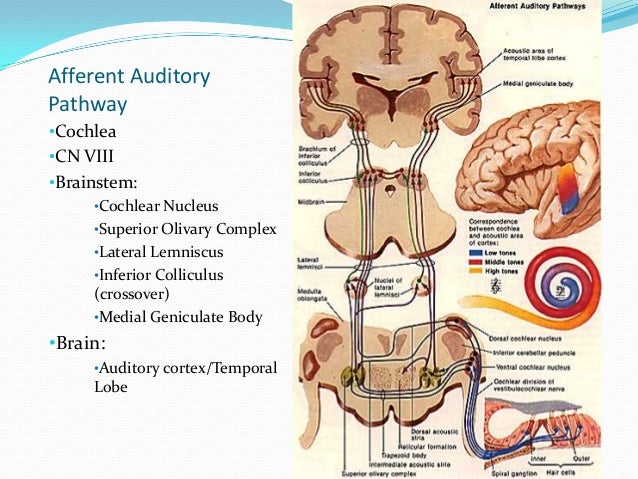
1 the lateral geniculate nucleus the major subcortical center relaying visual information to the primary visual cortex. Stimulus at one stage causes a response by an effector at a distinct stage. Unlike other systems the auditory system is not exclusively a crossed system it has both contralateral and ipsilateral inputs to the cortex.
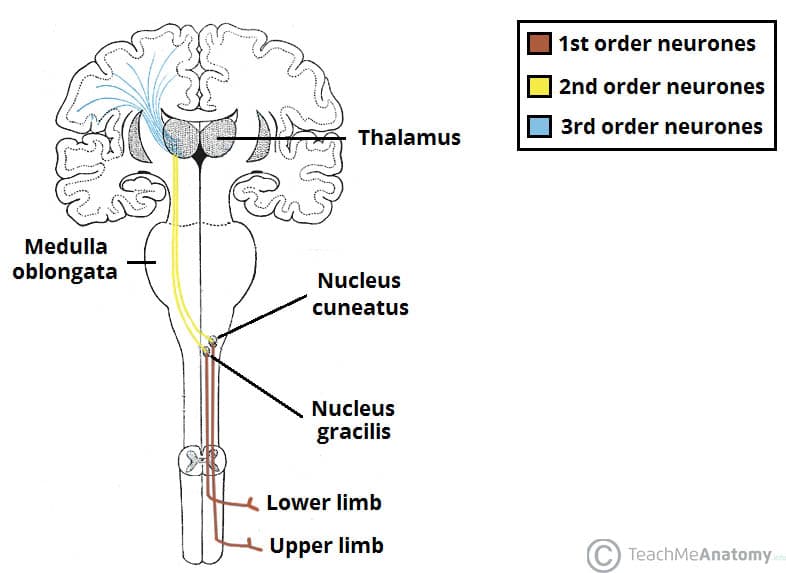
Central Nervous System Review Guidemwdocx. The _____ nervous system consists of visceral motor nerve fibers that regulate the activity of smooth muscles cardiac muscles and glands autonomic The autonomic nervous system is referred to as the. Ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and the contralateral nasal hemiretina.
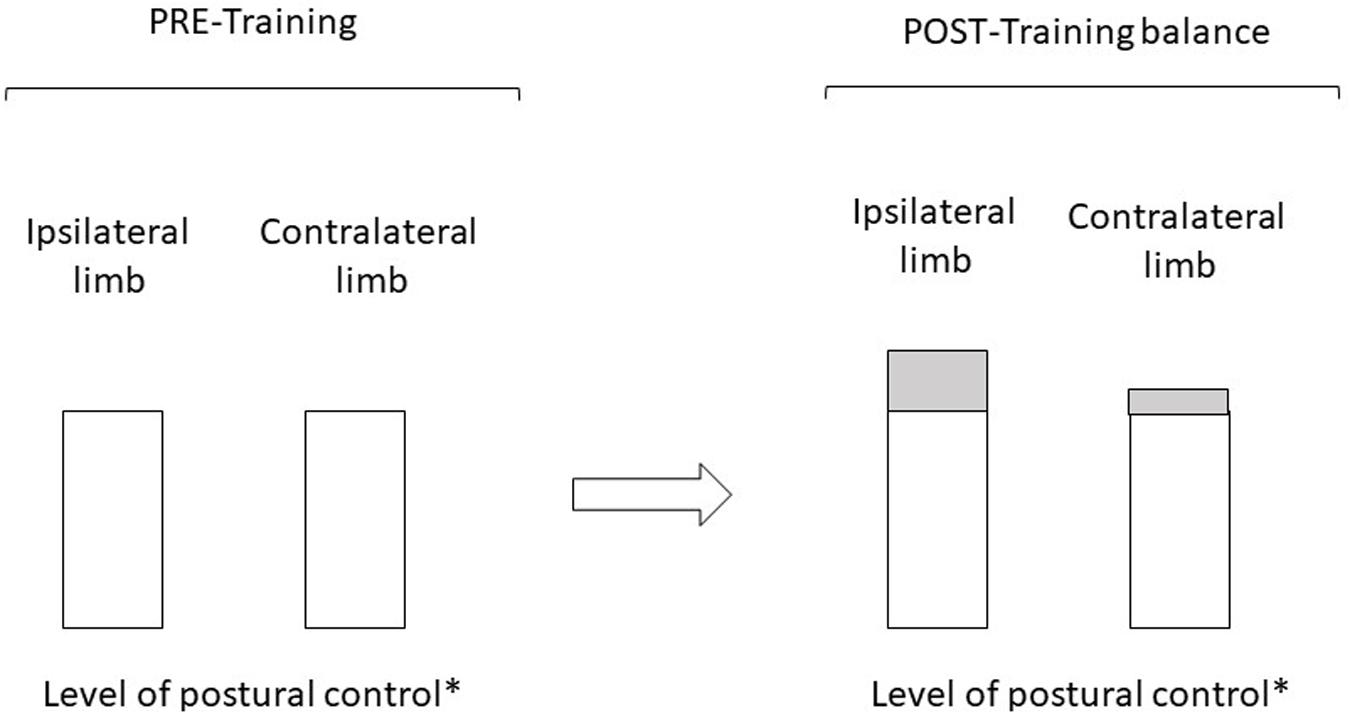
There is a general consensus that the mechanisms underlying the contralateral effect are mediated by adaptations of the central nervous system at supraspinal and spinal levels Zhou 2000Munn et. We have textbook solutions for you. At the same time the contralateral dorsal Y-group receives reduced excitation from contralateral vestibular primary afferents via a projection from the contralateral SVN see 5 Fig.
Reflex the place motor output occurs on reverse aspect of physique that stimulus is detected. Essentially the way I use it is if its a driving movement ipsilateral produces the greatest power production and stability meaning the right hand has the right leg back. The findings on contralateral sensitization including the increased contralateral second phase response to formalin whence spinal cord facilitation is known to be a component Puig and Sorkin.
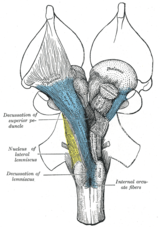
On the contralateral side the branches deliver synaptic currents first to the anterior regions closest to the midline and then to progressively more posterior regions. The crossed descending pathway from the contralateral dorsal Y-group not illustrated would reduce excitation of ipsilateral olivary neurons synergistically with increased inhibition from ipsilateral Psol. Contralateral work provides the greatest reach potential for pulling which means the.
J Pain Res. This trend is related to most ascending fibers at the low brainstem have not yet crossed to the other side hence a large portion of these fibers are ipsilateral not contralateral.
The crossed descending pathway from the contralateral dorsal Y-group not illustrated would reduce excitation of ipsilateral olivary neurons synergistically with increased inhibition from ipsilateral Psol.
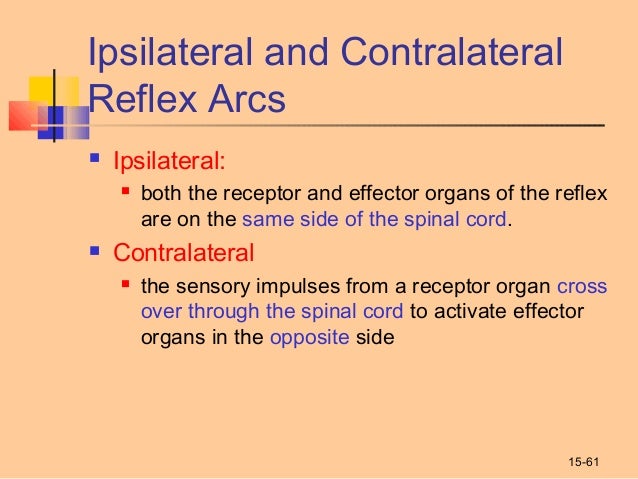
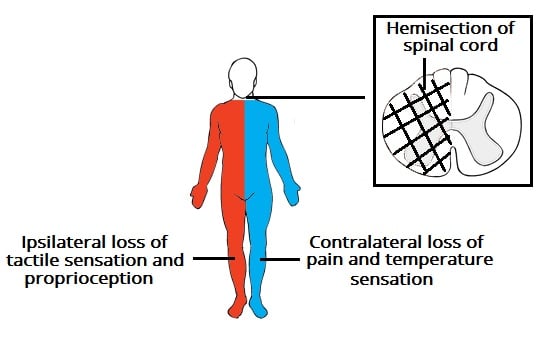
J Pain Res. Stimulus at one stage causes a response by an effector at a distinct stage. The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook. The ability of contralateral vibration to modify the right sensory thresholds suggests possible involvement of the central nervous system in vibratory modulation. Ipsilateral refers to structures on the same side of the body or brain left or right whereas contralateral refers to structures on opposite sides of the body. 2 the SII optical response to bilateral stimulation occupies both the anterior and posterior regions that responded to independent stimulation of the contralateral and. When an object lies superior to another it lies above it. As we found with ET-1 these changes were not caused by some systemically distributed factors but were clearly dependent on activity transmitted through the ipsilateral peripheral nervous system. The crossed descending pathway from the contralateral dorsal Y-group not illustrated would reduce excitation of ipsilateral olivary neurons synergistically with increased inhibition from ipsilateral Psol.
The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook. J Pain Res. 1 the optical response to contralateral stimulation occurs in a region more anterior in SII than does the response to ipsilateral stimulation. 2 the SII optical response to bilateral stimulation occupies both the anterior and posterior regions that responded to independent stimulation of the contralateral and. Reflex the place motor output occurs on reverse aspect of physique that stimulus is detected. The ability of contralateral vibration to modify the right sensory thresholds suggests possible involvement of the central nervous system in vibratory modulation. On the ipsilateral side the branches of the bushy cell axon are of equal length and thus deliver synaptic currents to their targets in the medial superior olive simultaneously.






























Post a Comment for "Ipsilateral And Contralateral Central Nervous System"